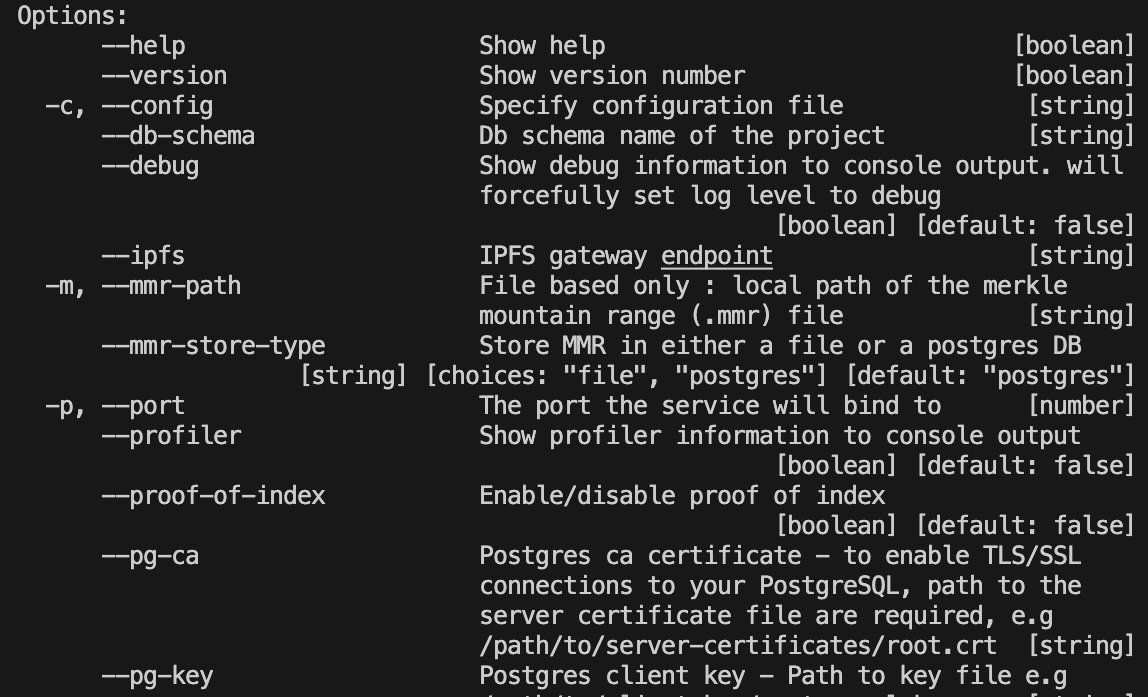
Sometimes the help within the command line can be a bit confusing as you can see below. Here I will explain what the various flags mean and also provide examples.
Options:
--help Show help [boolean]
--version Show version number [boolean]
-f, --subquery Local path of the subquery project [string]
--subquery-name Name of the subquery project [string]
-c, --config Specify configuration file [string]
--local Use local mode [boolean]
--batch-size Batch size of blocks to fetch in one round [number]
--timeout Timeout for indexer sandbox to execute the mapping
functions [number]
--debug Show debug information to console output. will
forcefully set log level to debug
[boolean] [default: false]
--profiler Show profiler information to console output
[boolean] [default: false]
--network-endpoint Blockchain network endpoint to connect [string]
--output-fmt Print log as json or plain text
[string] [choices: "json", "colored"]
--log-level Specify log level to print. Ignored when --debug is
used
[string] [choices: "fatal", "error", "warn", "info", "debug", "trace",
"silent"]
--migrate Migrate db schema (for management tables only)
[boolean] [default: false]
--timestamp-field Enable/disable created_at and updated_at in schema
[boolean] [default: true]
-d, --network-dictionary Specify the dictionary api for this network [string]Flags
–version
> subql-node --version
0.19.1
-f, –subquery
This flag is the most important because it actually starts the subquery node.
> subql-node -f . // starts project in current directory OR
> subql-node --subquery .–subquery-name TBA
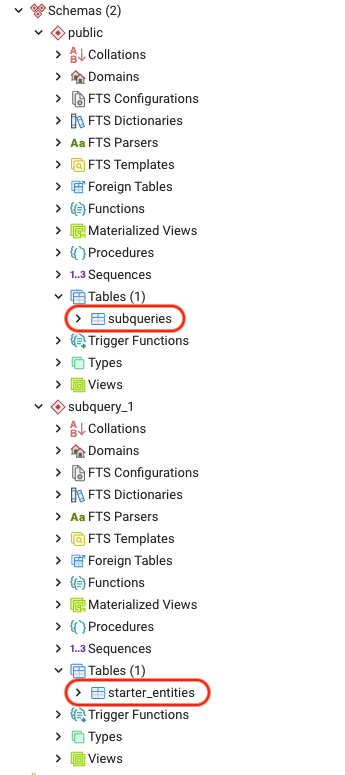
This flag is very interesting. When used it creates a seperate schema and starts the block synchronising from zero. It is almost creating another “instance” of your project.
> subql-node -f . --subquery-name=test1
> subql-node -f . --subquery-name=test2
> subql-node -f . --subquery-name=test3Will create 3 schemas as shown below.

-c, –config
This flag will read the various configurations explained here from a file. Create a yaml file with the following:
subquery: . // Mandatory. This is the local path of the project
subqueryName: hello // this is optional
batchSize: 55 // optional configName the file subquery_config.yml (the name does not matter). Place the file in the same directory as the project. The . means “the current directory”. Then with terminal in the project directory, run:
> subql-node -c ./subquery_config.yml–local
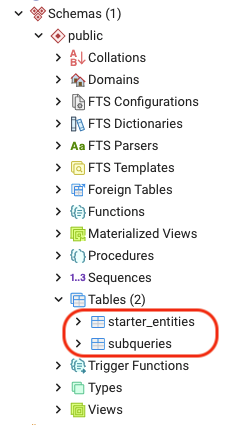
This flag is primarily used for debugging purposes where it creates the default starter_entity table in the default “postgres” schema.
subql-node -f . --localNote that once you use this flag, removing it won’t mean that it will point to another database. To repoint to another database you will have to create a NEW database and change the env settings to this new database. In other words, “export DB_DATABASE=<new_db_here>”
Without the local flag:
With the local flag:
–batch-size
> subql-node -f . --batch-size=20
2021-08-09T23:24:43.775Z <fetch> INFO fetch block [6601,6620], total 20 blocks
2021-08-09T23:24:45.606Z <fetch> INFO fetch block [6621,6640], total 20 blocks
2021-08-09T23:24:47.415Z <fetch> INFO fetch block [6641,6660], total 20 blocks
2021-08-09T23:24:49.235Z <fetch> INFO fetch block [6661,6680], total 20 blocks –timeout TBA
–debug
This show debug information to console output and forcefully sets the log level to debug.
> subql-node -f . --debug
2021-08-10T11:45:39.471Z <db> DEBUG Executing (1b0d0c23-d7c7-4adb-a703-e4e5c414e035): INSERT INTO "subquery_1"."starter_entities" ("id","block_height","created_at","updated_at") VALUES ($1,$2,$3,$4) ON CONFLICT ("id") DO UPDATE SET "id"=EXCLUDED."id","block_height"=EXCLUDED."block_height","updated_at"=EXCLUDED."updated_at" RETURNING "id","block_height","created_at","updated_at";
2021-08-10T11:45:39.472Z <db> DEBUG Executing (default): UPDATE "subqueries" SET "next_block_height"=$1,"updated_at"=$2 WHERE "id" = $3
2021-08-10T11:45:39.472Z <db> DEBUG Executing (1b0d0c23-d7c7-4adb-a703-e4e5c414e035): COMMIT; –profiler
This shows profiler information
subql-node -f . --local --profiler
2021-08-10T10:57:07.234Z <profiler> INFO FetchService, fetchMeta, 3876 ms
2021-08-10T10:57:08.095Z <profiler> INFO FetchService, fetchMeta, 774 ms
2021-08-10T10:57:10.361Z <profiler> INFO SubstrateUtil, fetchBlocksBatches, 2265 ms
2021-08-10T10:57:10.361Z <fetch> INFO fetch block [3801,3900], total 100 blocks
–network-endpoint
This flag allows users to override the network endpoint configuration from the manifest file.
subql-node -f . --network-endpoint="wss://polkadot.api.onfinality.io/public-ws"Note that the config in the manifest file is compulsory, otherwise you’ll get:
ERROR Create Subquery project from given path failed! Error: failed to parse project.yaml.
An instance of ProjectManifestImpl has failed the validation:
- property network has failed the following constraints: isObject
- property network.network has failed the following constraints: nestedValidation –output-fmt
> subql-node -f . --output-fmt=json
{"level":"info","timestamp":"2021-08-10T11:58:18.087Z","pid":24714,"hostname":"P.local","category":"fetch","message":"fetch block [10501,10600], total 100 blocks"}> subql-node -f . --output-fmt=colored
2021-08-10T11:57:41.480Z <subql-node> INFO node started
(node:24707) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead
2021-08-10T11:57:48.981Z <fetch> INFO fetch block [10201,10300], total 100 blocks
2021-08-10T11:57:51.862Z <fetch> INFO fetch block [10301,10400], total 100 blocks
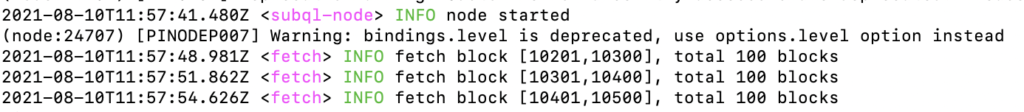
–log-level
There are 7 options to choose from. “fatal”, “error”, “warn”, “info”, “debug”, “trace”, “silent” as noted in the command line docs. The example below shows silent. The only way to tell if this is working or not is to query the database row count (select count(*) from subquery_1.starter_entities) or to query the block height.
Using other log levels will depend on if the code is outputting data at those log levels.
> subql-node -f . --log-level=silent
(node:24686) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead
(Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created)
(node:24686) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead
(node:24686) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead
(node:24686) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead
(node:24686) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead
(node:24686) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead
(node:24686) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead
(node:24686) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead
(node:24686) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead
(node:24686) [DEP0152] DeprecationWarning: Custom PerformanceEntry accessors are deprecated. Please use the detail property.
(node:24686) [PINODEP007] Warning: bindings.level is deprecated, use options.level option instead–migrate TBA
–timestamp-field
–timestamp-field=false removes the created_at and updated_at columns.
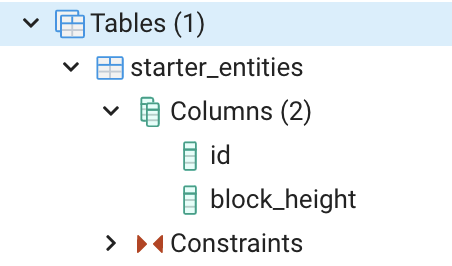
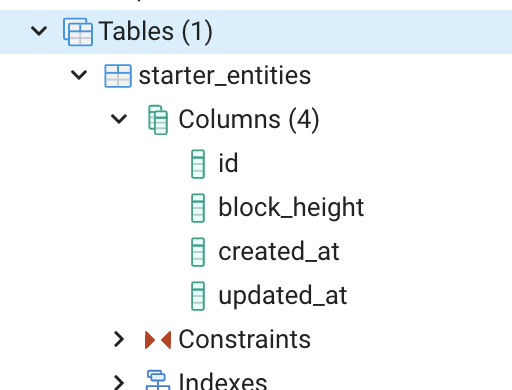
-d, –network-dictionary
This allows you to specify a dictionary endpoint which is a free service that is provided and hosted at: https://explorer.subquery.network/ (search for dictionary) and presents an API endpoint of: https://api.subquery.network/sq/subquery/dictionary-polkadot
Typically this would be set in your manifest file but below shows an example of using it as an argument in the command line.
subql-node -f . -d "https://api.subquery.network/sq/subquery/dictionary-polkadot"